2025 Top 10 Rapid Prototyping Techniques Driving Innovation in Engineering
In the fast-evolving landscape of engineering, rapid prototyping has emerged as a critical catalyst for innovation, enabling engineers to transform ideas into tangible products with unprecedented speed and efficiency. According to Dr. Emily Chen, a renowned expert in the field of additive manufacturing, "Rapid prototyping not only accelerates the design process, but also fosters creativity by allowing engineers to iterate and refine concepts in real-time." This sentiment encapsulates the essence of rapid prototyping, highlighting its role in pushing the boundaries of what is possible in modern engineering.
As we delve into the top 10 rapid prototyping techniques shaping the future of engineering by 2025, it becomes evident that these methods are not solely about speed. They represent a paradigm shift in how teams collaborate, test, and evolve their designs. From 3D printing and CNC machining to digital twins and virtual reality simulations, these techniques are redefining the innovation landscape, allowing for greater flexibility and responsiveness to market demands.

In this exploration, we will uncover the transformative potential of these rapid prototyping techniques, examining how they empower engineers to not only meet current challenges but also anticipate future needs. As technology continues to advance, the synergy between rapid prototyping and engineering innovation will undoubtedly pave the way for remarkable advancements in various industries.
Emerging Trends in 3D Printing for Rapid Prototyping in 2025
In 2025, the landscape of rapid prototyping is expected to be significantly shaped by emerging trends in 3D printing technology. As the industry continues to evolve, we see a clear trajectory pointing towards innovative methods that enhance speed and efficiency in product development. Technologies such as digital light processing (DLP) and multi-material 3D printing are making it easier than ever for engineers to create complex geometries with fine details, ultimately driving creativity and reducing time to market.
Furthermore, the market for 3D printed satellites is projected to expand, with estimates suggesting a market size worth USD 1582.6 million by 2034. This growth, fuelled by a staggering compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 27.23% during this period, highlights the increasing reliance on additive manufacturing in aerospace applications. Companies leveraging these advances in 3D printing not only stand to benefit from cost savings but also from the flexibility and customization these technologies offer. As we move towards 2035, the 3D printing market is set to grow exponentially, from $18.5 billion in 2025 to an impressive $93.7 billion, indicating that innovation in rapid prototyping will remain a cornerstone of engineering advancements.
2025 Top 10 Rapid Prototyping Techniques Driving Innovation in Engineering
| Technique | Description | Applications | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) | A method that builds parts layer by layer using thermoplastic materials. | Aerospace, Automotive, Prototyping | Cost-effective, versatile material options | Limitations in resolution and strength |
| Stereolithography (SLA) | An additive manufacturing process using photopolymer resins and UV light. | Jewelry, Medical Devices, Complex Prototypes | High precision and surface finish | Long curing times, costly resins |
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | Uses laser to sinter powdered materials into solid structures. | Functional Prototypes, Aerospace Components | Strong, complex designs without supports | Expensive setup, post-processing required |
| Digital Light Processing (DLP) | A 3D printing technology using light to cure resin layers rapidly. | Rapid Prototyping, Dental Models | Speed and high fidelity | Limited material options, lower durability |
| PolyJet Printing | Spray layers of photopolymer wax for detailed models. | Consumer Products, Automotive Parts | Multi-material and color capabilities | Expensive materials, post-production challenges |
| Binder Jetting | Uses a binding agent to join powder materials. | Metal Parts, Sand Casting | High-speed printing, diverse materials | Less strength than other methods, post-processing required |
| Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM) | Layers of adhesive-coated paper or plastic are laminated together. | Architectural Models, Physical Mock-ups | Cost-effective for large models | Limited resolution, not suitable for functional parts |
| 3D Metal Printing | Involves layer-by-layer melting and fusing of metallic powders. | Aerospace Components, Medical Implants | High strength and complex geometries | High cost and need for specialized equipment |
| Vacuum Casting | Uses silicone molds to create parts from liquid plastic. | Low-volume production, Product Design Validation | Smooth finishes, fast production | Not suitable for mass production |
Advancements in CNC Machining Techniques for Precision Engineering
CNC machining has revolutionized the landscape of precision engineering, paving the way for rapid prototyping techniques that enhance innovation across various sectors. According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global CNC machining market was valued at approximately $70 billion in 2020 and is projected to reach $118 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 7.6%. This growth is driven by the continuous demand for high-quality, precise components across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
Incorporating advanced CNC techniques, such as multi-axis machining and adaptive control systems, significantly improves production efficiency while achieving tighter tolerances. For instance, multi-axis CNC machining allows for the creation of complex geometries in a single setup, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional manufacturing methods. This procedural innovation not only enhances productivity but also supports the rapid turnaround needed for effective prototyping.
Tip: To maximize the benefits of CNC machining in your projects, invest in employee training on the latest software and machine capabilities. This education ensures that your team can leverage the full potential of modern CNC technology to overcome the challenges of precision engineering.
Staying updated with the latest trends and advancements in CNC machining is crucial. Engaging in regular industry seminars and workshops can provide insights into emerging techniques and technologies, further solidifying your competitive edge in the rapidly evolving engineering landscape.
Integrating AI and Machine Learning in Rapid Prototyping Processes
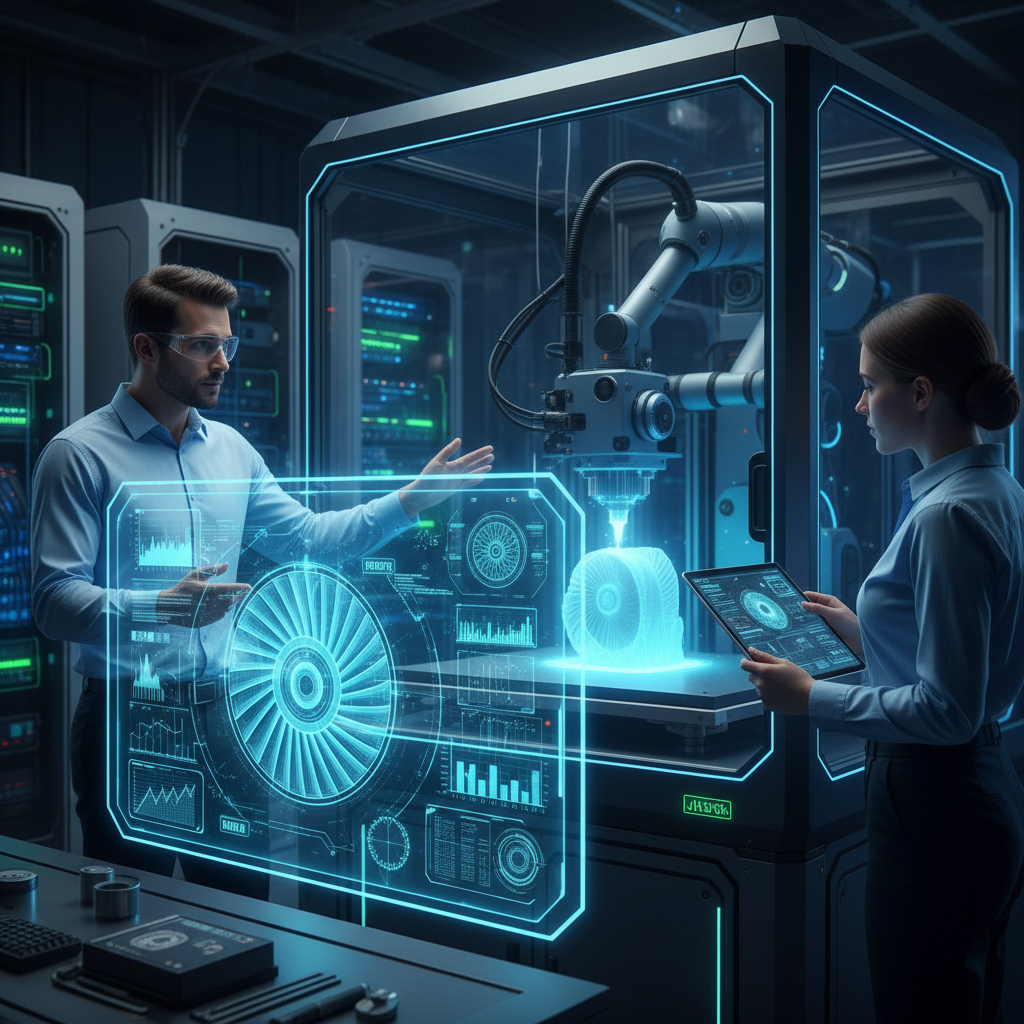

The integration of AI and machine learning into rapid prototyping processes is set to revolutionize engineering innovation by 2025. According to a recent report from Grand View Research, the global rapid prototyping market is expected to reach $16.2 billion by 2028, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 15.5%. This growth is largely driven by the introduction of AI technologies that enhance design accuracy and speed of prototyping. Machine learning algorithms can rapidly analyze vast datasets to predict material behavior and performance, significantly reducing the time required for iterative testing.
To optimize the benefits of AI in rapid prototyping, engineers should consider investing in advanced software tools that facilitate machine learning integration. Such tools can automate numerous design processes, allowing teams to focus on creativity and innovation. Additionally, maintaining a diverse dataset is essential, as it improves the accuracy of machine learning predictions. The integration of AI not only accelerates development cycles but also enables the rapid iteration of prototypes, making it easier to pivot designs based on real-time feedback.
Tip: To harness the full potential of AI in rapid prototyping, prioritize upskilling your team in data analysis and machine learning fundamentals. This knowledge will enable them to leverage these technologies effectively, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within your engineering projects.
Sustainable Materials Revolutionizing Rapid Prototyping Practices
The burgeoning field of rapid prototyping is witnessing a significant transformation, driven by the adoption of sustainable materials. According to a report by Smithers Pira, the global market for sustainable materials in the 3D printing sector is projected to reach $1.4 billion by 2025. As industries increasingly prioritize eco-friendly practices, innovators are integrating biopolymers and recycled materials into their prototyping processes, minimizing environmental impact without sacrificing performance.
In addition to addressing environmental concerns, sustainable materials enhance the capabilities of rapid prototyping. For instance, natural fiber composites, which can reduce weight while maintaining strength, are gaining traction in sectors like automotive and aerospace. A study by the American Society for Testing and Materials indicates that these materials can cut carbon emissions by up to 70% compared to traditional plastics. Furthermore, advancements in technology allow for the use of materials derived from agricultural byproducts, paving the way for a circular economy that benefits both manufacturers and the environment. This shift not only fosters innovation but also aligns with the growing demand for sustainability in engineering practices.
2025 Top 10 Rapid Prototyping Techniques Driving Innovation in Engineering
This chart illustrates the frequency of usage (in percentage) of various rapid prototyping techniques projected for the year 2025. Techniques such as 3D Printing and CNC Machining are expected to lead in popularity due to their efficiency and adaptability in engineering and design processes.
Virtual and Augmented Reality Enhancing Prototyping Visualization and Testing
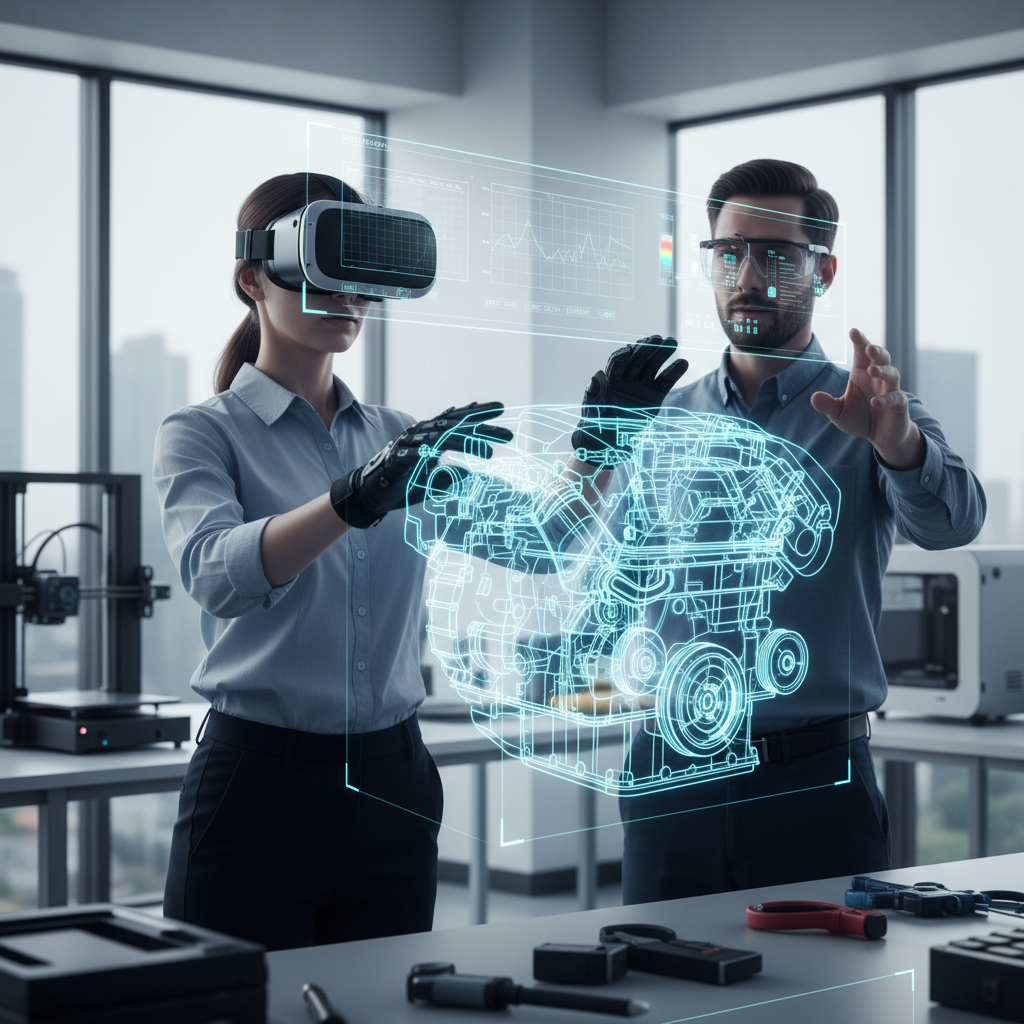

Virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR) are revolutionizing the way engineers approach prototyping by enhancing visualization and testing processes. Traditional prototyping often involves physical models that require significant resources and time to produce. With the integration of VR and AR, engineers can create immersive simulations that allow for real-time interaction with digital prototypes. This capability not only streamlines the design process but also enables teams to identify potential issues early, reducing the risk of costly modifications later in development.
Moreover, VR and AR facilitate collaborative efforts among teams, regardless of their physical location. Engineers can share their visualizations in a virtual environment, enabling stakeholders to engage with and evaluate designs without the need for physical prototypes. This dynamic interaction fosters innovative ideas and designs, as feedback can be gathered instantaneously during virtual meetings. As these technologies continue to evolve, their impact on rapid prototyping will undoubtedly lead to increased efficiency and creativity in engineering practices, paving the way for groundbreaking developments.
Related Posts
-

Top Strategies for Enhancing Rapid Prototyping Efficiency
-

Why Rapid Prototyping is Essential for Modern Product Development Success
-

How to Revolutionize Your Production Process with Advanced Manufacturing Technology
-

Ultimate Guide to Precision Injection Molding for Global Buyers in 2023
-
How to Achieve Optimal Results with Precision Injection Techniques
-

The Future of US Injection Molding: Innovations Shaping Tomorrow's Manufacturing
