How to Choose the Right Mold Manufacturing Process for Your Needs?
Choosing the right mold manufacturing process is crucial for your project. Each method has unique advantages and challenges. The decision can significantly impact production quality, cost, and timeline.
Mold manufacturing varies widely, from injection molding to compression techniques. Understanding your specific needs is essential. Are you aiming for high volume or intricate designs? Factors like material type and desired finish matter too.
Mistakes can happen during selection. Some may prioritize cost over quality. Others might overlook the importance of lead time. Reflecting on these aspects can lead to better choices in mold manufacturing.
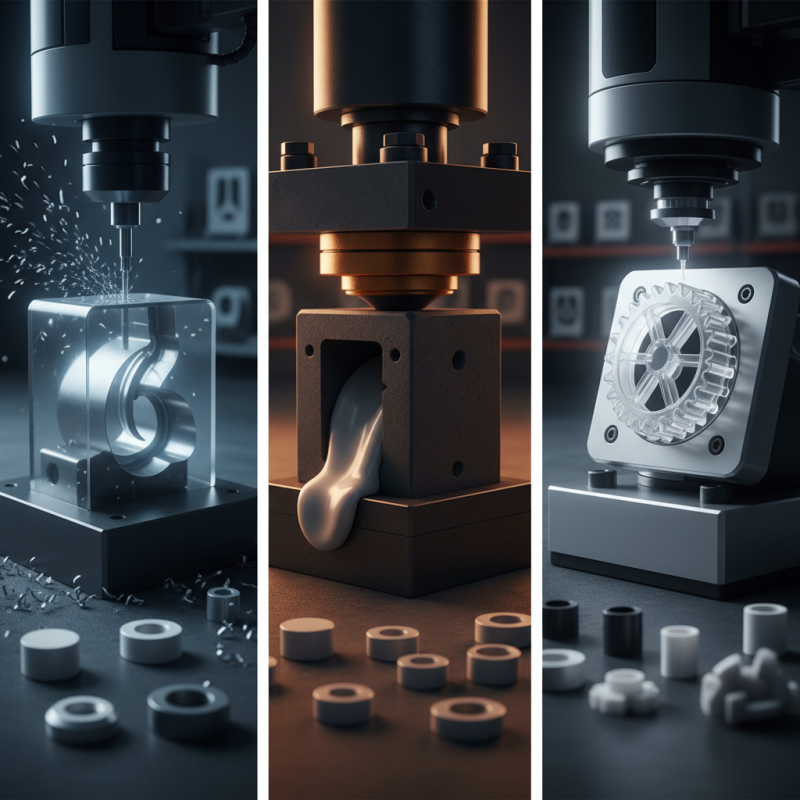

Understanding Different Mold Manufacturing Processes
When selecting a mold manufacturing process, understanding the various methods is crucial. There are several processes, such as injection molding, blow molding, and compression molding. Each has its unique strengths and weaknesses. For instance, injection molding is efficient for high-volume production, but the initial setup costs can be significant. Conversely, compression molding may be suitable for smaller batches, yet it lacks the speed of other methods.
Tips: Always evaluate the volume of production needed. If you're looking for high quantities, injection molding is often the best choice. However, if your project is more niche, consider alternative methods. Don't overlook the materials available. The choice can drastically affect the cost and durability of your molds.
Understanding how each process works will help you make informed decisions. Injection molding allows for intricate designs but requires precise specifications. On the other hand, blow molding is great for hollow objects but might not suit detailed shapes. Reflect on the complexity of your product. Some methods can fall short of expectations if the design is too intricate for the chosen process. Remember, mulling over these details can save time and money later.
Understanding Different Mold Manufacturing Processes
Evaluating Key Factors for Selecting a Mold Manufacturing Method
Choosing the right mold manufacturing process is crucial. Several key factors must guide your decision. Consider the product's complexity. Intricate designs may require advanced techniques. Simpler products could suit basic methods. Evaluate production volume as well. High volumes might justify costlier options like injection molding. Lower quantities could lean towards 3D printing for efficiency.
Material selection also plays a vital role. Different processes accommodate varying materials. For example, thermoplastics are common in injection molding. However, resin-based techniques excel in detail. Think about lead times too. Some methods are quicker but may compromise precision. In contrast, meticulous processes can slow down production.
Cost is another major factor. Analyze your budget carefully. Expensive processes may not always be the best choice. Explore all available methods. Each option has pros and cons. As a final thought, continuously reassess your choice. Needs may change, leading to better solutions. Keep an open mind for future adjustments. Evaluate feedback from previous projects to refine your approach.
How to Choose the Right Mold Manufacturing Process for Your Needs?
| Mold Manufacturing Process | Ideal Material | Production Volume | Lead Time | Cost per Unit | Surface Finish |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection Molding | Thermoplastics | High | 4-6 weeks | $0.50 - $5.00 | Good |
| 3D Printing | Various Polymers | Low to Medium | 1-4 weeks | $10 - $50 | Moderate |
| Compression Molding | Rubber and Thermosets | Medium to High | 3-5 weeks | $1.00 - $4.00 | Fair |
| Blow Molding | Polyethylene, PVC | Medium to High | 6-8 weeks | $0.25 - $2.00 | Good |
| Die Casting | Aluminum, Zinc | High | 8-12 weeks | $1.50 - $10.00 | Excellent |
Comparative Analysis of Injection Molding and Other Techniques

When selecting a mold manufacturing process, understanding the differences is crucial. Injection molding stands out for high-volume production. It creates complex shapes with precision. However, it may not be the best choice for low-volume runs. The initial costs can be high due to mold design and fabrication.
In contrast, techniques like 3D printing offer flexibility. They allow rapid prototyping and adjustments. With 3D printing, the lead time is shorter. Yet, the material options can be limited. The finish might not match injection molding quality. This trade-off requires careful consideration based on project needs.
Other methods, like blow molding and compression molding, present their own challenges. Blow molding is ideal for hollow objects but demands specific material types. Compression molding works well for certain thermosets but varies in cycle times. Each method has advantages and limitations that can impact production efficiency. Making the right choice depends on balancing quality, volume, and cost.
Assessing Cost, Time, and Material Considerations in Mold Making
Choosing the right mold manufacturing process requires careful consideration of cost, time, and materials. According to a report by the International Association of Plastics Distribution, nearly 45% of companies cite cost as the primary concern in mold selection. Understanding the balance between cost and quality can be complex. Low-cost options may require more frequent replacements, leading to higher long-term expenses.
Time is another critical factor. The average lead time for mold production can range from a few weeks to several months. Many manufacturers face pressure to meet tight deadlines. A survey found that nearly 30% of firms experienced delays due to poor planning in the mold manufacturing process. Delays can significantly affect market competitiveness. Fast-tracking the process may compromise quality and increase costs, presenting a dilemma.
Material choice further complicates the decision. Various materials, like steel and aluminum, each has unique advantages. Steel molds often last longer but come with a higher initial cost. In contrast, aluminum molds are quicker to manufacture but may not withstand high-volume production. According to industry data, 70% of professionals acknowledge the challenges of material selection. Each choice needs careful evaluation, balancing strength, durability, and cost. This reflection is crucial for optimal decision-making.
Identifying Industry-Specific Requirements for Mold Production
When selecting a mold manufacturing process, understanding specific industry requirements is crucial. Different sectors have varying standards and expectations. For instance, the automotive industry often prioritizes durability and precision. It may require molds that can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. According to a report by the Society of Automotive Engineers, nearly 70% of manufacturers face challenges in meeting these stringent standards.
In contrast, the consumer electronics sector focuses more on aesthetics and intricate designs. Molds used in this industry must accommodate tight tolerances and unique geometries. A study from the Consumer Technology Association reveals that 60% of companies in this field struggle to adapt their mold-making processes to rapid design changes. Companies frequently overlook the importance of flexibility in their tooling systems, leading to increased costs and extended lead times.
Moreover, quality control is often a neglected aspect in mold production. Many manufacturers do not invest adequately in inspection technologies. As per data from the MoldMaking Technology magazine, over 40% of mold makers report issues with dimensional accuracy. This can result in significant production delays and increased waste. Identifying these industry-specific nuances is vital to making informed decisions about the right mold manufacturing process.
Related Posts
-

Ultimate Guide to Achieving High Molding Precision in Manufacturing
-

Exploring Injection Moulding Process Innovations at the 138th China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

Top 10 FAQs About Injection Molding: What You Need to Know
-
2025 Guide: How to Accelerate Product Development with Rapid Prototyping Injection Molding
-

How to Use Rapid Prototyping with Injection Molding for Fast Product Development
-
10 Best Injection Molding Techniques for Maximizing Efficiency in Production
