How to Achieve Molding Precision in Manufacturing Processes
Achieving molding precision is a critical goal in manufacturing processes. John Smith, a leading expert in this field, emphasizes, “Precision molds lead to better product outcomes.” His insight highlights the importance of accurate mold creation.
Molding precision impacts product quality, cost efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Small errors can result in significant defects, prompting costly rework. Focusing on molding precision means understanding the entire production process. It involves selecting the right materials, equipment, and techniques. Manufacturers must also be willing to adapt and learn from mistakes.
Despite advancements, achieving perfect molding precision remains a challenge. Variations in temperature and pressure can negatively affect results. Continuous refinement and testing are essential for improvement. As manufacturers strive for excellence, they must confront imperfections. Only by addressing these issues can they improve overall precision and quality.

Understanding Molding Precision in Manufacturing Processes
Molding precision is crucial in manufacturing processes. It directly affects product quality and performance. Achieving this requires a deep understanding of material properties, process parameters, and environmental factors. Every detail counts. For instance, even a tiny temperature fluctuation can lead to dimensional changes in the final product. It’s essential to monitor conditions closely.
In practice, achieving molding precision can be challenging. Variations in raw materials, machine calibration issues, and human error often come into play. Even with strict protocols, imperfections may arise. Regular audits and quality checks can help identify these flaws early. However, overlooking minor discrepancies can lead to significant issues later. Continuous improvement should be a goal for manufacturers.
Proper training for operators is vital. They need to understand both the processes and the importance of precision. However, ensuring consistent training is not always practical. Sometimes, operators may miss key details, impacting the outcome. Over time, pinpointing these gaps can lead to better strategies for enhancement. Addressing human factors is as important as refining technical processes. Molding precision is a journey of constant learning and adaptation.
Key Factors Influencing Molding Accuracy
Achieving molding precision is critical in manufacturing processes. Various key factors influence molding accuracy. One major factor is the material used. For example, thermosetting plastics typically offer better dimensional stability than thermoplastics. Studies show that material choice can affect accuracy by up to 25%.
Temperature control during the molding process also plays a vital role. Inconsistent temperatures can lead to warping and defects, adversely impacting output quality. Data suggests that maintaining a stable temperature can improve molding precision by 15%.
Tip: Regularly calibrate your temperature sensors for optimal performance. Another essential aspect is mold design. Complex geometries may complicate the manufacturing process and lead to inaccuracies. Simpler designs tend to yield more consistent results.
Reflecting on past projects can reveal persistent issues. For instance, molds that were not designed with appropriate release angles caused production delays and increased waste. Continuous evaluation of these factors can greatly enhance molding precision in future projects.
Techniques for Enhancing Molding Precision
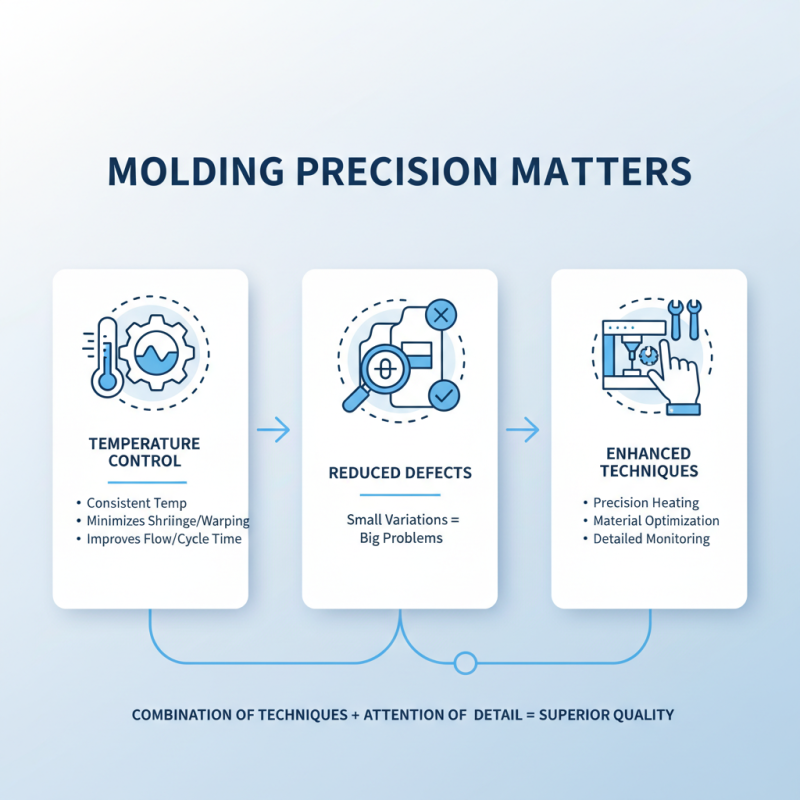
Achieving molding precision is vital in manufacturing. Small variations can lead to significant product defects. Therefore, enhancing molding precision requires a combination of techniques and attention to detail. One effective technique is temperature control. Keeping the mold at a consistent temperature minimizes material shrinkage and warping. Proper heating can improve flow rates and reduce cycle times. Yet, inconsistencies in temperature can still occur, leading to flaws.
Another important technique is the use of advanced design technology. Computer-aided design (CAD) software helps in creating accurate mold designs. This technology can simulate various factors affecting the molding process, from material selection to cooling times. However, relying solely on software can lead to overconfidence. It's crucial to validate designs with real-world prototypes to identify potential issues.
Regular maintenance of molding equipment is essential too. Even minor wear and tear can affect precision. Regular checks and calibrations can help prevent unexpected breakdowns and discrepancies. While these practices significantly enhance precision, they require constant effort. Manufacturers must be willing to reflect on their processes and make adjustments as necessary. The pursuit of high precision is ongoing.
Challenges in Achieving High Precision Molding
Achieving high precision in molding processes presents a myriad of challenges. Material selection plays a critical role. The wrong material can lead to warping and dimensional inaccuracies. In fact, studies indicate that over 30% of defects in molded products stem from improper material choices. This often reflects a lack of understanding of material properties, resulting in costly waste and rework.
Temperature control is another common obstacle. Variations in temperature during the molding process can lead to uneven cooling. According to industry reports, as much as 25% of production can be impacted by inadequate temperature management. This issue may arise from outdated machinery or insufficient training for operators. Manual adjustments often fail to create the necessary consistency.
Tool wear and maintenance also complicate precision. As tools degrade, they can alter the dimensions of molds, leading to imprecise outputs. Reports show that nearly 20% of manufacturers do not monitor tool condition adequately. This lack of vigilance can result in significant downtime and increased costs. Regular maintenance schedules might need reevaluation. These reflections reveal that achieving molding precision is not merely a technical challenge but also a matter of pressing improvement in operational practices.
Challenges in Achieving High Precision Molding
This bar chart illustrates the challenges faced in achieving high precision molding during manufacturing processes. Each category highlights the importance of factors such as material variability, temperature control, mold wear, injection speed, and cooling time, indicating their impact levels on the overall molding precision.
Future Trends in Molding Precision Technologies
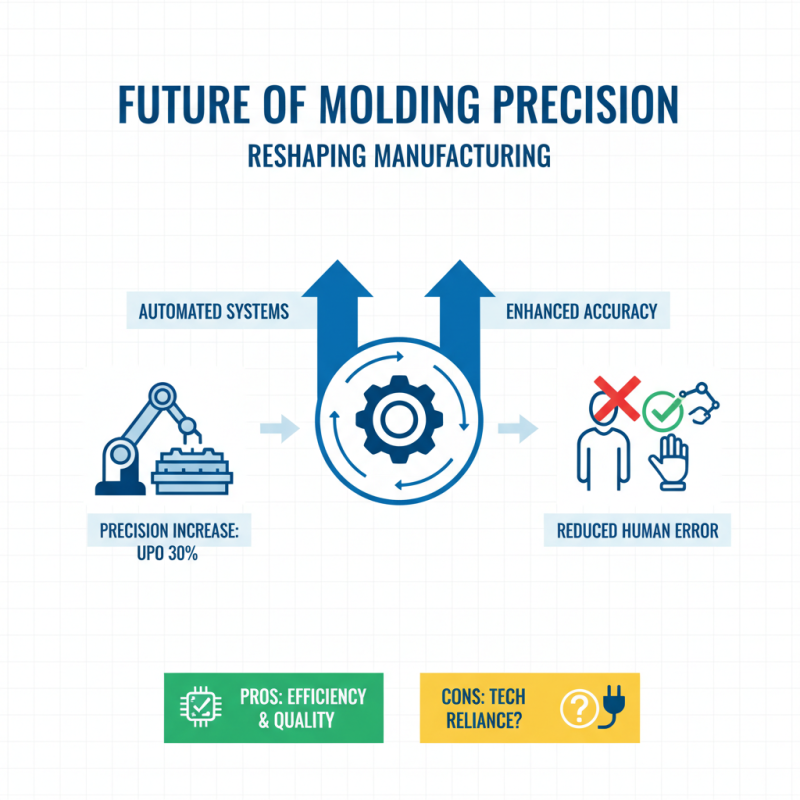
Future trends in molding precision technologies are reshaping the manufacturing landscape. Advancements in automated systems promise enhanced accuracy. Reports suggest that automated molding processes increase precision by up to 30%. This shift reduces human error but also raises questions about the potential for over-reliance on technology.
Additive manufacturing techniques are on the rise. These methods, such as 3D printing, allow for complex geometries. A recent study revealed that these innovations can cut lead times by half. However, the materials used often require ongoing improvement to ensure durability and performance.
As industry standards evolve, the need for sustainable practices grows. The demand for eco-friendly materials is evident, with a 15% increase reported in research-focused on biodegradable options. Yet, manufacturers face challenges in balancing sustainability and precision. It's a growing concern that needs addressing as we move forward.
Related Posts
-

Ultimate Guide to Precision Injection Molding for Global Buyers in 2023
-

Understanding the Role of Precision Injection in Modern Manufacturing
-
Understanding the Impact of Molding Precision on Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
-

Unlocking Efficiency: The Key Benefits of Contract Injection Molding for Manufacturing Success
-

Contract Injection Molding Opportunities at 2025 China Import and Export Fair with Market Growth Projections
-
2025 Guide: How to Accelerate Product Development with Rapid Prototyping Injection Molding
